Learn how to connect your nodegoat environment to Transkribus and other services
CORE Admin
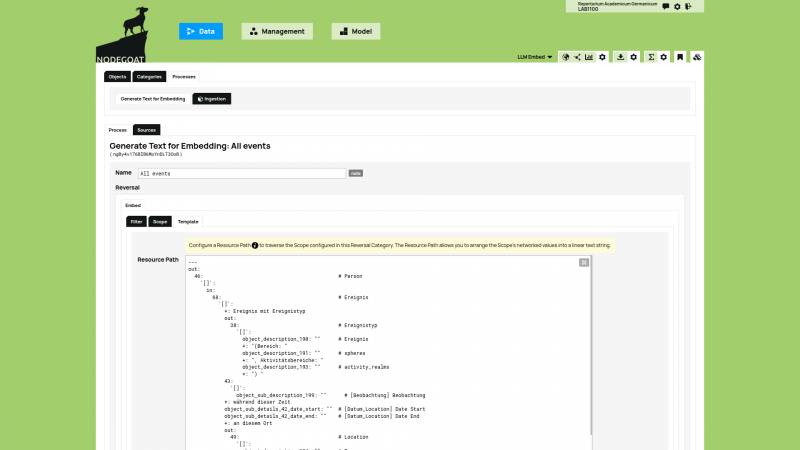
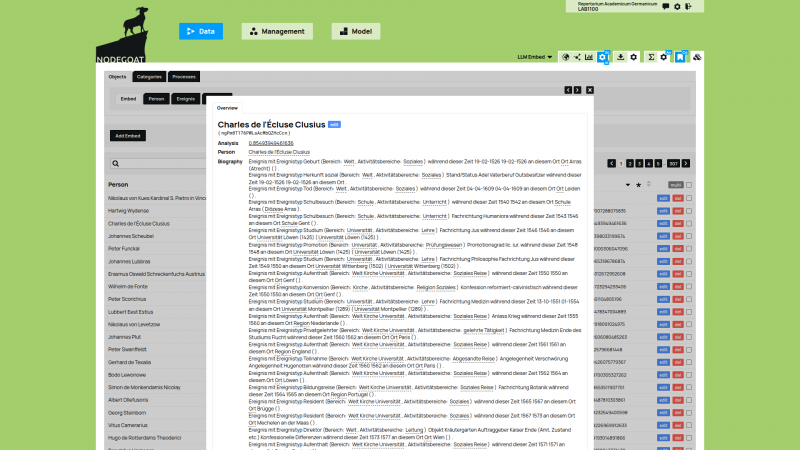
The nodegoat Guides have been extended with a new section on 'Ingestion Processes'. An Ingestion Process allows you to query an external resource and ingest the returned data in your nodegoat environment. Once the data is stored in nodegoat, it can be used for tagging, referencing, filtering, analysis, and visualisation purposes.
You can ingest data in order to gather a set of people or places that you intend to use in your research process. You can also ingest data that enriches your own research data. Any collection of primary sources or secondary sources that have been published to the web can be ingested as well. This means that you can ingest transcription data from Transkribus, or your complete (or filtered) Zotero library.
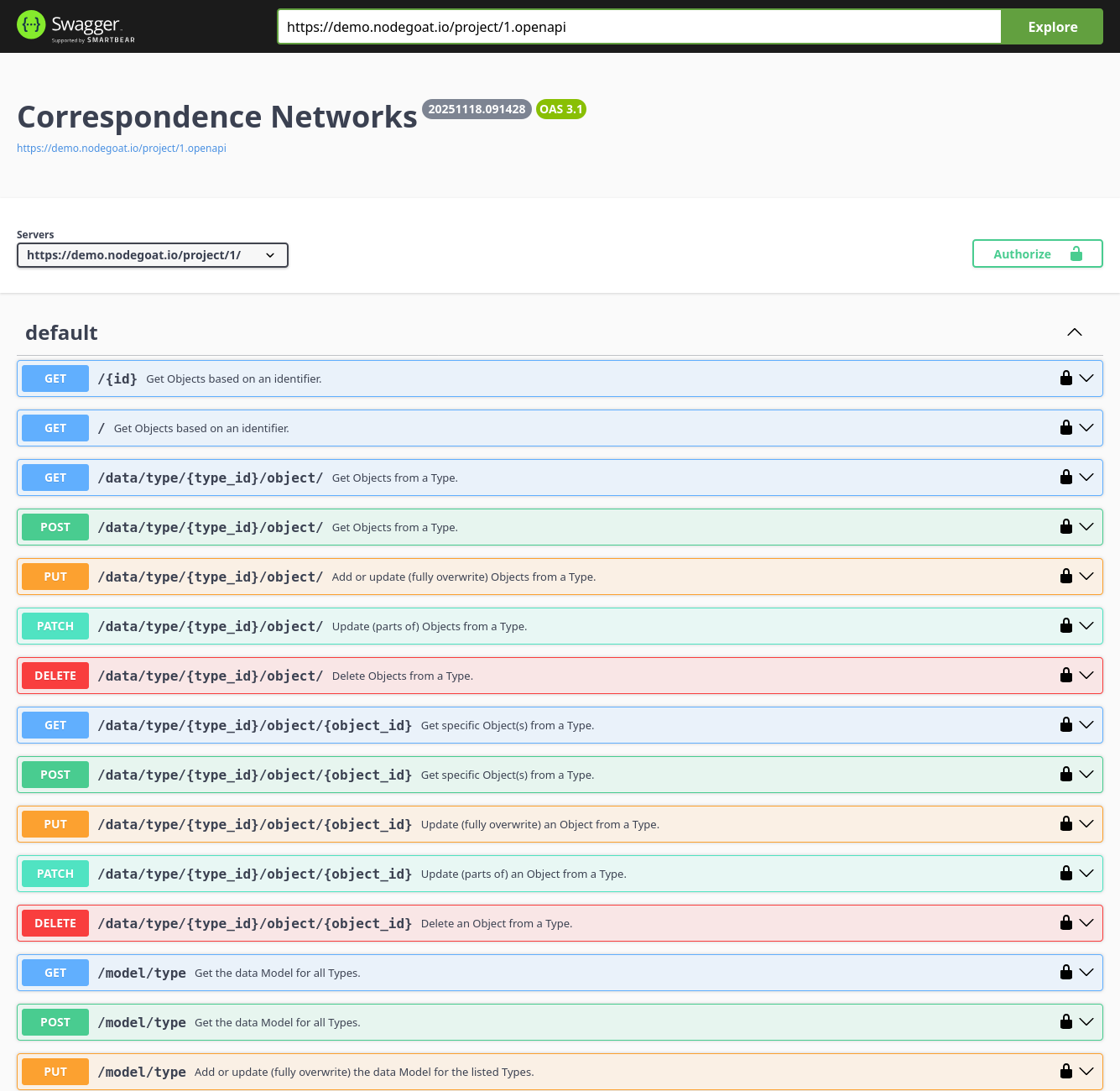
The development of the Ingestion Process was part of the project 'Dynamic Data Ingestion (DDI)' and builds upon the Linked Data Resource feature, initially commissioned by the TIC-project in 2015 and extended in collaboration with ADVN in 2019. Every nodegoat user is able to make use of these features. Every endpoint that outputs JSON or XML can be queried. nodegoat data can be exported in CSV and ODT formats, or published via the nodegoat API as JSON and JSON-LD.